
Git Lfs Command Line
To associate a file type in your repository with Git LFS, enter git lfs track followed by the name of the file extension you want to automatically upload to Git LFS. For example, to associate a.psd file, enter the following command: $ git lfs track '.psd' Adding path.psd. When you try to use GitHub Desktop to clone a repository that you do not have write access to, GitHub Desktop will prompt you to create a fork automatically. You can choose to use your fork to contribute to the original upstream repository or to work independently on your own project.
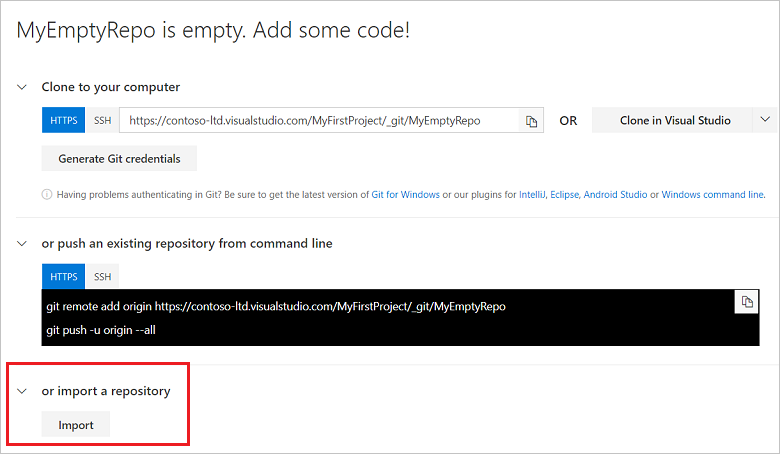
You can use GitHub to clone remote repositories to GitHub Desktop.
Git Lfs Github Desktop
Tip: You also can use GitHub Desktop to clone repositories that exist on GitHub. For more information, see 'Cloning a repository from GitHub Desktop.'
Sign in to GitHub and GitHub Desktop before you start to clone.
On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository.
Above the list of files, click Code.
Click Open with GitHub Desktop to clone and open the repository with GitHub Desktop.
Click Choose... and, using the Finder window, navigate to a local path where you want to clone the repository.
Note: If the repository is configured to use LFS, you will be prompted to initialize Git LFS.
Click Clone.
Github Desktop Git Lfs
Git Lfs Command Line
To associate a file type in your repository with Git LFS, enter git lfs track followed by the name of the file extension you want to automatically upload to Git LFS. For example, to associate a.psd file, enter the following command: $ git lfs track '.psd' Adding path.psd. When you try to use GitHub Desktop to clone a repository that you do not have write access to, GitHub Desktop will prompt you to create a fork automatically. You can choose to use your fork to contribute to the original upstream repository or to work independently on your own project.
You can use GitHub to clone remote repositories to GitHub Desktop.
Git Lfs Github Desktop
Tip: You also can use GitHub Desktop to clone repositories that exist on GitHub. For more information, see 'Cloning a repository from GitHub Desktop.'
Sign in to GitHub and GitHub Desktop before you start to clone.
On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository.
Above the list of files, click Code.
Click Open with GitHub Desktop to clone and open the repository with GitHub Desktop.
Click Choose... and, using the Finder window, navigate to a local path where you want to clone the repository.
Note: If the repository is configured to use LFS, you will be prompted to initialize Git LFS.
Click Clone.
Github Desktop Git Lfs
Sign in to GitHub and GitHub Desktop before you start to clone.
On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository.
Above the list of files, click Code.
Click Open with GitHub Desktop to clone and open the repository with GitHub Desktop.
Click Choose... and, using Windows Explorer, navigate to a local path where you want to clone the repository.
Note: If the repository is configured to use LFS, you will be prompted to initialize Git LFS.
Click Clone.
